Puerto Rico
Stadistical data
-
Official name: Puerto Rico
-
Languages: Spanish (Official).
-
Capital: San Juan
-
Population: 3,264,000
-
Internet penetration: 78%
-
Internet country code: .pr
-
Ethnic groups: Whites, mestizos, african descent.
-
Total areal: 8,870 km2
-
Political division: 78 municipality
-
Currency: U.S. dollar
-
GDP per capita (USD): $32,640.71

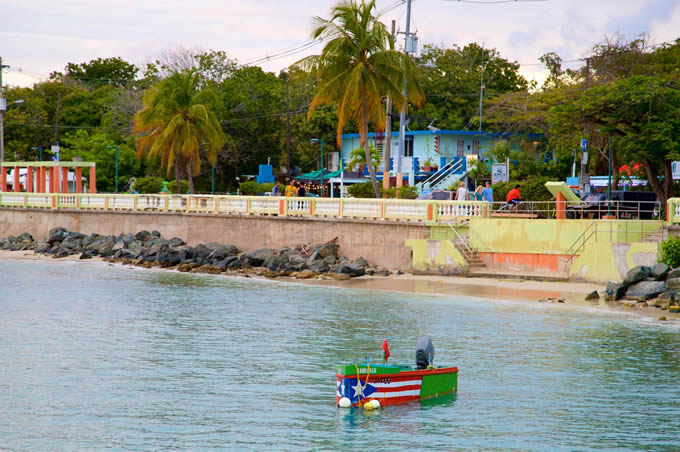
Major cities
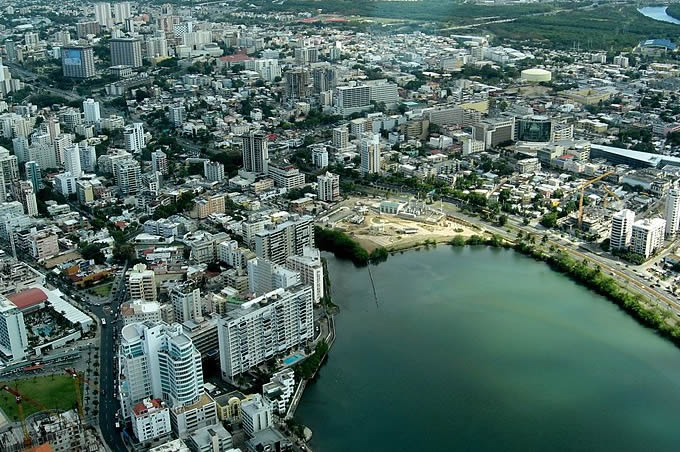
San Juan
Capital and largest city of Puerto Rico, located on the north coast of the island on the Atlantic Ocean. A major port and tourist spot of the West Indies, it is the oldest city now under US jurisdiction. At the beginning of the 16th century, San Juan was the starting point for Spanish expeditions to the unknown parts of the New World.
Its fortifications drove out the English navigator Sir Francis Drake in 1595 as well as subsequent attackers, but George Clifford, 3rd Earl of Cumberland briefly captured it in 1598 and a Dutch force took the town from the landward side in 1625. In In response, the fortress of San Cristóbal, the largest Spanish fort in the New World, was built to the northeast and, from 1634 to 1638, walls were erected along the southern part of the city, facing the port.
The bastions that exist today were greatly added to during the period of 1765-83. In 1885 there was an uprising against the Spanish administration and in May 1898 the cannons of San Cristóbal engaged a US fleet. to bombard the city. Puerto Rico became a territory of the U.S.A. under the terms of the Treaty of Paris, that same year.
The San Juan National Historic Site (1949) includes the Morro and San Cristóbal fortifications; this area, along with La Fortaleza, was designated a World Heritage Site in 1983.
The main campus of the University of Puerto Rico (1903) is located in the Barrio Río Piedras (guardian) of San Juan. In 1957 the university became the home of the Casals Festival (now held in Santurce, the suburb's main residence), founded by Spanish cellist Pablo Casals.
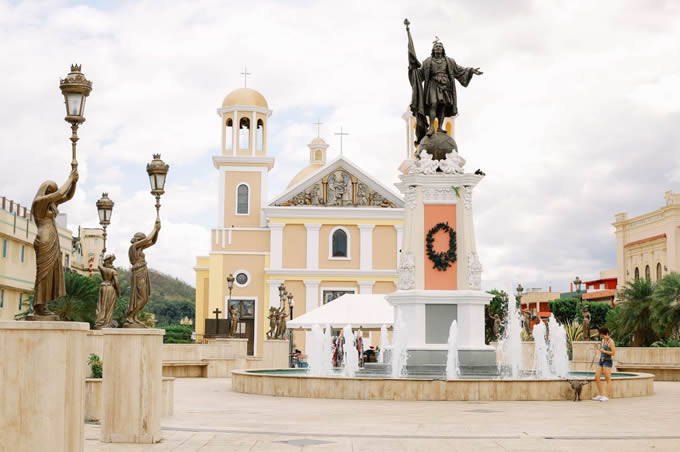
Ponce
Ponce is located in the foothills of the Cordillera Central de Puerto Pico, west of the Llano Costanero del Sur. The plain is formed by the consolidation of the lower parts of the valleys that descend to the south from the Central Cordillera and the Sierra de Cayey and extends uninterruptedly from Patillas to Ponce.
The Municipality of Ponce covers an area of 116 square miles (300 square kilometers). It borders to the north with the municipalities of Adjuntas, Utuado and Jayuya; to the east with Juana Díaz; and to the west with Peñuelas. To the south it borders the Caribbean Sea. Ponce's climate is tropical semi-desert, with an average temperature of 77' F. (25 0 C) and an annual precipitation of 40 inches (102cm) of rain.
The Municipality is located in the temperature zone called “tierra caliente" (tropical) that corresponds to the plains and low hills of the country. It is one of the driest areas of Puerto Rico. This is evident in the type of vegetation and in the low flow of the rivers and streams that cross the territory, which remain basically dry during almost the entire year.
According to the 1990 census, the Municipality of Ponce has a population of 210,000 inhabitants, which makes it the third most populous in the country, after San Juan (449,285) and Bayamón (221,815).
Guatemala
Edificio Géminis 10, Torre Sur, #1702
Guatemala, Guatemala.
Honduras
Tegucigalpa
Col. Rubén Darío, Calle Venecia, #2152
Tegucigalpa, Honduras.
San Pedro Sula
Blvd. Los Próceres, #238
San Pedro Sula, Honduras.
El Salvador
Col. Escalón, 3ra Calle Poniente, Pasaje Stahl, #147
San Salvador, El Salvador.
Nicaragua
Bolonia, del canal 2, 2 cuadras abajo, 30 vrs al sur, #24
Managua, Nicaragua.
Costa Rica
75mts sur de la entrada al Blvd. Los Yoses, #76
San José, Costa Rica.
Panamá
San Francisco, Calle 64 y Las Caracuchas, #12
Panamá, Panamá.
Dominican Republic
Paseo de Los Indios, #49, El Millón
Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic.
- info@mercaplan.com
- jobs@mercaplan.com
- 2023 - MERCAPLAN Central America and the Caribbean





